1Q70.10 • Simple Machines: Gears
Location: Cabinet 1
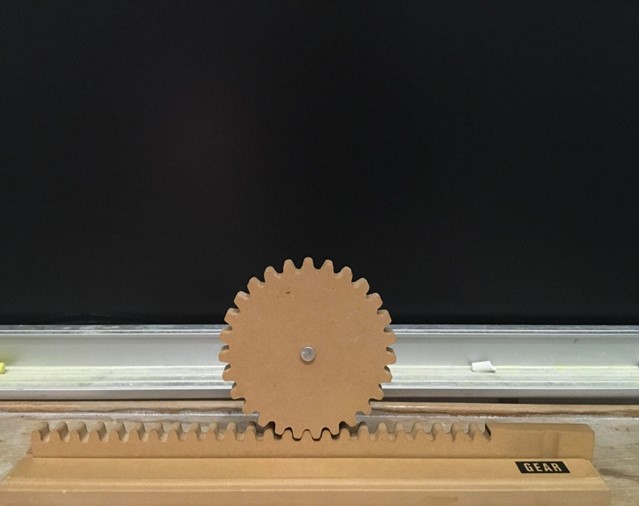
REGULAR GEAR
Concepts Conveyed:
- Gears can convert translational motion into rotational motion and vice versa.
Instructions / Notes:
-
Experiment 1: Rotational motion turns into translational motion
- Position the gear at the end of the post where the last tooth is located.
- Rotate the gear to demonstrate translational motion occurring with the post; you can rotate the gear left or right however you see fit.
-
Experiment 2: Translational motion turns into rotational motion
- Position the gear in the middle of the post.
- Move the post left to right to show the gear rotation about the post; you can also see that as you move the post from left to right, the gear rotates counterclockwise.
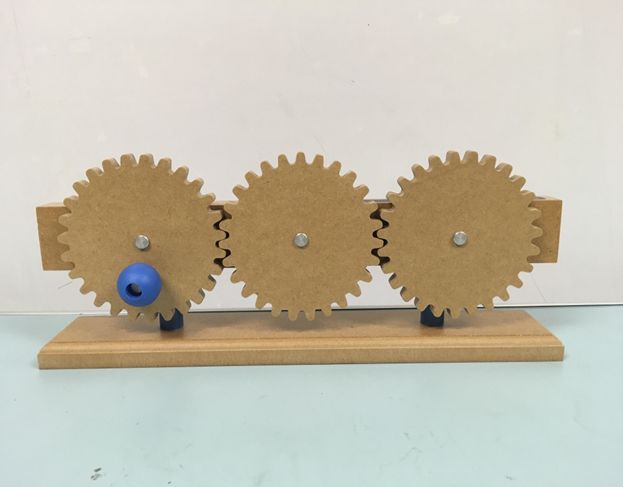
GEAR TRAIN
Concepts Conveyed:
- Complex machines consist of simple machines that convert energy to do work
- The amount of work done depends on the amount of energy present
- Mechanical Advantage: A way of measuring how much easier it is to do work or how
much less force is required.
- Wheels & axles: increase mechanical advantage by covering a larger area using force; the larger the wheel the greater the mechanical advantage
Instructions / Notes:
- Use the hand crank to turn the first gear clockwise
- Notice the direction of rotation of both follower gears
All photos of the demo used at the University of Texas at Austin
Last updated on February 25, 2025